이 매뉴얼은 JK전자(JK Electronics) 에 의해서 번역, 수정, 작성 되었고 소유권 또한
JK전자(JK Electronics)의 것입니다. 소유권자의 허가를 받지 않고 무단으로 수정, 삭제하거나 배포 할 수 없습니다.
S3C6410 Start Kit Linux 콘솔 어플리케이션 Developer Guide
* Update history
- 2011.1.13 : 초기 Release
1. Environment Setup
1.1 Installation Fedora9
S3C6410 Startkit 의 모든 예제와 컴파일 과정은 VMWare에 설치된 Fedora9 머신에서 실행 하였습니다. 다른
리눅스 환경에서는 테스트 되지 않았습니다. 폐도라 리눅스의 전체 설치 과정은 여기 Installation
Fedora9 을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
1.2 Install cross-build compiler
AM용 임베디드 리눅스의 어플리케이션을 개발하기 위해서는 컴파일러로 개발용 Linux PC에 ARM용 크로스 컴파일러를 설치 해야 합니다. 이 개발보드를 위해서는 arm-linux-gcc-4.5.1 컴파일러를 설치 해야 합니다. 이 컴파일러는 armv6 Instruction set and support hardware floating-point operations 등을 지원 합니다. 자세한 설치 방법은 리눅스 개발자 가이드를 참조하시기 바랍니다.1. Linux 개발자 가이드(커널 컴파일, 파일시스템, Qt 포팅 등)
개발보드에 대한 모든 콘솔 어플리케이션 소스는 CD/Linux/examples-mini6410-20111119.tgz 파일로 압축이 되어 있습니다.
2. Example of embedded Linux applications
2.1 Hello, World!
Hello, World 예제의 소스코드는 "/opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/examples/hello"
에 있습니다.
| #include
<stdio.h> int main(void) { printf("hello, FriendlyARM!\n"); } |
Step1 : Compile Hello, World
# cd
/opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/examples/hello
# make
컴파일이 완료된 바이너리 파일의 정보를 볼 수 있습니다.
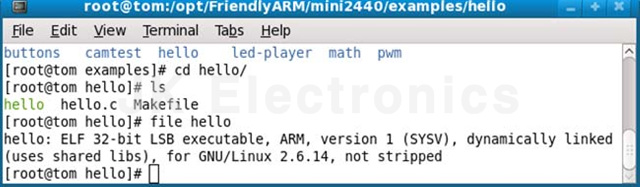
Step2 : Download Hello, World example to development board
개발보드에 컴파일된 예제를 다운로드 하는 방법에는 4가지 정도의 방법이 있습니다.
(1) FTP를 이용한 다운로드하는 방법
(2) USB 메모리 or SD 메모리 카드를 이용해서 타겟 보드에 마운트 후 복사하는 방법
(3) 시리얼 포트를 이용해서 다운로드 하는 방법
(4) NFS를 이용해서 바로 실행 하는 방법
(1) FTP를 이용한 다운로드하는 방법 (recommended)
아래와 같이 개발용 Linux PC에서 타겟 보드에 FTP로 접속후 다운로드 합니다.
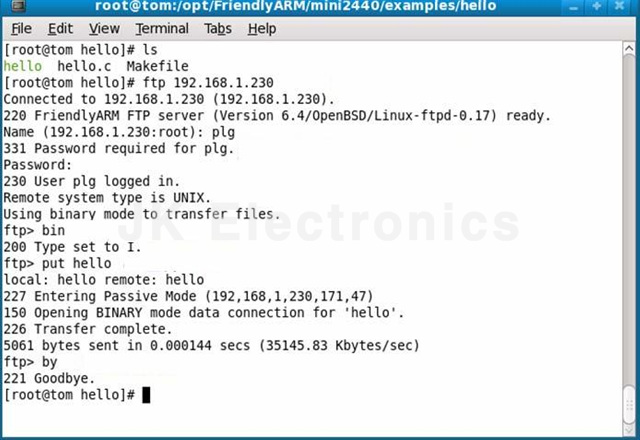
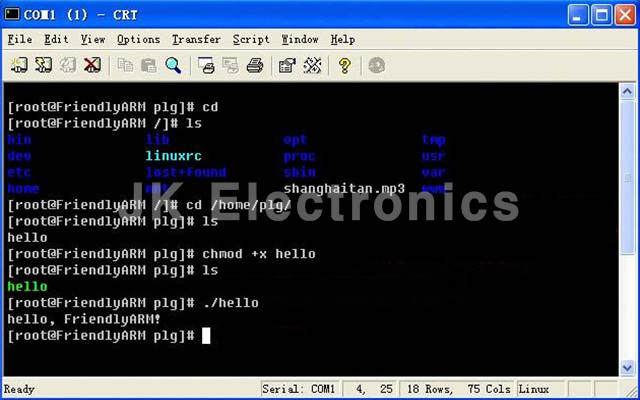
다운로드가 완료되면 타겟 보드에서 다운로드한 파일에 실행 권한을 부여 합니다.
(2) USB 메모리 or SD 메모리 카드를 이용해서 타겟 보드에 마운트 후 복사하는 방법
PC에서 아래 명령을 이용해서 USB 메모리를 마운트 한다음 예제 파일을 USB메모리에 복사합니다.
# mount /dev/sda1 /mnt
# cp hello /mnt
# umount /mnt
USB 메모리를 타겟 개발보드에 연결 하면 자동으리 /udisk로 마운트가 되고 아래과 같은 명령으로 실행 해 볼 수 있습니다.
# cd /udisk
# ./hello
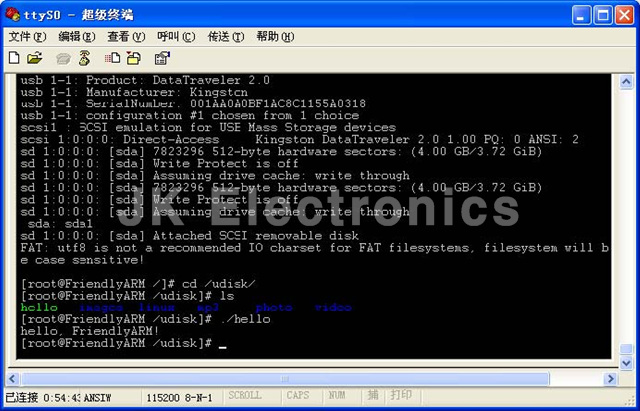
(3) 시리얼 포트를 이용해서 다운로드 하는 방법
시리얼을 통한 파일 다운로드 하는 방법은 리눅스 사용자 가이드 "1.2.4 시리얼 포트를 이용한 PC파일 전송" 을 참조하시기
바랍니다.
다운로드한 파일에 실행 권한을 부여 합니다.
# chmod +x hello
(4) NFS를 이용해서 바로 실행 하는 방법
"192.168.1.111" 는 NFS서버 PC의 IP 주소 입니다.
# mount -t nfs -o nolock
192.168.1.111:/opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/rootfs_qtopia_qt4 /mnt
NFS마운트가 성공적으로 연결이 되면 /mnt 디렉토리에 NFS서버의
"opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/rootfs_qtopia_qt4" 디렉토리가 마운트 되어 접근 할 수
있습니다.
# cd /mnt
# ./hello
2.2 LED Test Program
| 드라이버 소스 파일 이름 | mini6410_leds.c |
| Device Type | misc |
| Device Name | /dev/leds |
| 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/examples/leds |
| 예제 이름 | led.c |
| 예제 실행 파일 이름 | led |
| LED driver has been compiled into the default kernel, so can not be loaded using insmod. | |
| #include
<stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> int main(int argc, char **argv) { int on; int led_no; int fd; /* check led control of two parameters, if no parameter input is out. */ if (argc != 3 || sscanf(argv[1], "%d", &led_no) != 1 || sscanf(argv[2],"%d", &on) != 1 || on < 0 || on > 1 || led_no < 0 || led_no > 3) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: leds led_no 0|1\n"); exit(1); } /* open /dev/ leds device file */ fd = open("/dev/leds0", 0); if (fd < 0) { fd = open("/dev/leds", 0); } if (fd < 0) { perror("open device leds"); exit(1); } /* the ioctl system call and input the parameter control led */ ioctl(fd, on, led_no); /* close the device handle */ close(fd); return 0; } |
|
컴파일하고 타겟보드에 다운로드 해서 실행하는 방법은 Hello, World 예제와 동일 합니다.
2.3 Button Test Program
| 드라이버 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/linux-2.6.36/drivers/char |
| 드라이버 소스 파일 이름 | Mini6410_buttons.c |
| Device Type | misc |
| Device Name | /dev/buttons |
| 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/examples/buttons |
| 예제 이름 | buttons_test.c |
| 예제 실행 파일 이름 | buttons |
| Button driver has been compiled into the default kernel, so can not be loaded using insmod. | |
| #include
<stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/select.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <errno.h> int main(void) { int buttons_fd; char buttons[6] = {'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0'}; buttons_fd = open("/dev/buttons", 0); if (buttons_fd < 0) { perror("open device buttons"); exit(1); } for (;;) { char current_buttons[6]; int count_of_changed_key; int i; if (read(buttons_fd, current_buttons, sizeof current_buttons) != sizeof current_buttons) { perror("read buttons:"); exit(1); } for (i = 0, count_of_changed_key = 0; i < sizeof buttons / sizeof buttons[0]; i++) { if (buttons[i] != current_buttons[i]) { buttons[i] = current_buttons[i]; printf("%skey %d is %s", count_of_changed_key? ", ": "", i+1, buttons[i] == '0' ? "up" : "down"); count_of_changed_key++; } } if (count_of_changed_key) { printf("\n"); } } close(buttons_fd); return 0; } |
|
2.4 PWM Buzzer Test Program
| 드라이버 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/linux-2.6.36/drivers/char |
| 드라이버 소스 파일 이름 | Mini6410_pwm.c |
| Device Type | misc |
| Device Name | /dev/pwm |
| 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/examples/pwm |
| 예제 이름 | pwm_test.c |
| 예제 실행 파일 이름 | Pwm_test |
| PWM driver has been compiled into the default kernel, so can not be loaded using insmod. | |
| #include
<stdio.h> #include <termios.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define PWM_IOCTL_SET_FREQ 1 #define PWM_IOCTL_STOP 2 #define ESC_KEY 0x1b static int getch(void) { struct termios oldt,newt; int ch; if (!isatty(STDIN_FILENO)) { fprintf(stderr, "this problem should be run at a terminal\n"); exit(1); } // save terminal setting if(tcgetattr(STDIN_FILENO, &oldt) < 0) { perror("save the terminal setting"); exit(1); } // set terminal as need newt = oldt; newt.c_lflag &= ~( ICANON | ECHO ); if(tcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO,TCSANOW, &newt) < 0) { perror("set terminal"); exit(1); } ch = getchar(); // restore termial setting if(tcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO,TCSANOW,&oldt) < 0) { perror("restore the termial setting"); exit(1); } return ch; } static int fd = -1; static void close_buzzer(void); static void open_buzzer(void) { fd = open("/dev/pwm", 0); if (fd < 0) { perror("open pwm_buzzer device"); exit(1); } // any function exit call will stop the buzzer atexit(close_buzzer); } static void close_buzzer(void) { if (fd >= 0) { ioctl(fd, PWM_IOCTL_STOP); close(fd); fd = -1; } } static void set_buzzer_freq(int freq) { // this IOCTL command is the key to set frequency int ret = ioctl(fd, PWM_IOCTL_SET_FREQ, freq); if(ret < 0) { perror("set the frequency of the buzzer"); exit(1); } } static void stop_buzzer(void) { int ret = ioctl(fd, PWM_IOCTL_STOP); if(ret < 0) { perror("stop the buzzer"); exit(1); } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int freq = 1000 ; open_buzzer(); printf( "\nBUZZER TEST ( PWM Control )\n" ); printf( "Press +/- to increase/reduce the frequency of the BUZZER\n" ) ; printf( "Press 'ESC' key to Exit this program\n\n" ); while( 1 ) { int key; set_buzzer_freq(freq); printf( "\tFreq = %d\n", freq ); key = getch(); switch(key) { case '+': if( freq < 20000 ) freq += 10; break; case '-': if( freq > 11 ) freq -= 10 ; break; case ESC_KEY: case EOF: stop_buzzer(); exit(0); default: break; } } } |
|
2.5 I2C-EEPROM programming example
| 드라이버 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/linux-2.6.36/drivers/i2c/busses |
| 드라이버 소스 파일 이름 | I2c-s3c2410.c |
| Device Type | Char device |
| Device Name | /dev/i2c/0 |
| 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/examples/i2c |
| 예제 이름 | eeprog.c 24cXX.c |
| 예제 실행 파일 이름 | i2c |
| PWM driver has been compiled into the default kernel, so can not be loaded using insmod. | |
| #include
<stdio.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <getopt.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include "24cXX.h" #define usage_if(a) do { do_usage_if( a , __LINE__); } while(0); void do_usage_if(int b, int line) { const static char *eeprog_usage = "I2C-24C08(256 bytes) Read/Write Program, ONLY FOR TEST!\n" "FriendlyARM Computer Tech. 2009\n"; if(!b) return; fprintf(stderr, "%s\n[line %d]\n", eeprog_usage, line); exit(1); } #define die_if(a, msg) do { do_die_if( a , msg, __LINE__); } while(0); void do_die_if(int b, char* msg, int line) { if(!b) return; fprintf(stderr, "Error at line %d: %s\n", line, msg); fprintf(stderr, " sysmsg: %s\n", strerror(errno)); exit(1); } static int read_from_eeprom(struct eeprom *e, int addr, int size) { int ch, i; for(i = 0; i < size; ++i, ++addr) { die_if((ch = eeprom_read_byte(e, addr)) < 0, "read error"); if( (i % 16) == 0 ) printf("\n %.4x| ", addr); else if( (i % 8) == 0 ) printf(" "); printf("%.2x ", ch); fflush(stdout); } fprintf(stderr, "\n\n"); return 0; } static int write_to_eeprom(struct eeprom *e, int addr) { int i; for(i=0, addr=0; i<256; i++, addr++) { if( (i % 16) == 0 ) printf("\n %.4x| ", addr); else if( (i % 8) == 0 ) printf(" "); printf("%.2x ", i); fflush(stdout); die_if(eeprom_write_byte(e, addr, i), "write error"); } fprintf(stderr, "\n\n"); return 0; } int main(int argc, char** argv) { struct eeprom e; int op; op = 0; usage_if(argc != 2 || argv[1][0] != '-' || argv[1][2] != '\0'); op = argv[1][1]; fprintf(stderr, "Open /dev/i2c/0 with 8bit mode\n"); die_if(eeprom_open("/dev/i2c/0", 0x50, EEPROM_TYPE_8BIT_ADDR, &e) < 0, "unable to open eeprom device file " "(check that the file exists and that it's readable)"); switch(op) { case 'r': fprintf(stderr, " Reading 256 bytes from 0x0\n"); read_from_eeprom(&e, 0, 256); break; case 'w': fprintf(stderr, " Writing 0x00-0xff into 24C08 \n"); write_to_eeprom(&e, 0); break; default: usage_if(1); exit(1); } eeprom_close(&e); return 0; } |
|
2.6 Serial Programming Example
| 드라이버 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/linux-2.6.36/drivers/serial/ |
| 드라이버 소스 파일 이름 | S3c6400.c |
| Device Name | /dev/ttySAC0,1,2,4 |
| 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/examples/comtest |
| 예제 이름 | comtest.c |
| 예제 실행 파일 이름 | armcomtest |
| Test program compiled x86 version and arm version available, and its source code is exactly the same | |
| # include
<stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <termio.h> # include <unistd.h> # include <fcntl.h> # include <getopt.h> # include <time.h> # include <errno.h> # include <string.h> static void Error(const char *Msg) { fprintf (stderr, "%s\n", Msg); fprintf (stderr, "strerror() is %s\n", strerror(errno)); exit(1); } static void Warning(const char *Msg) { fprintf (stderr, "Warning: %s\n", Msg); } static int SerialSpeed(const char *SpeedString) { int SpeedNumber = atoi(SpeedString); # define TestSpeed(Speed) if (SpeedNumber == Speed) return B##Speed TestSpeed(1200); TestSpeed(2400); TestSpeed(4800); TestSpeed(9600); TestSpeed(19200); TestSpeed(38400); TestSpeed(57600); TestSpeed(115200); TestSpeed(230400); Error("Bad speed"); return -1; } static void PrintUsage(void) { fprintf(stderr, "comtest - interactive program of comm port\n"); fprintf(stderr, "press [ESC] 3 times to quit\n\n"); fprintf(stderr, "Usage: comtest [-d device] [-t tty] [-s speed] [-7] [-c] [-x] [-o] [-h]\n"); fprintf(stderr, " -7 7 bit\n"); fprintf(stderr, " -x hex mode\n"); fprintf(stderr, " -o output to stdout too\n"); fprintf(stderr, " -c stdout output use color\n"); fprintf(stderr, " -h print this help\n"); exit(-1); } static inline void WaitFdWriteable(int Fd) { fd_set WriteSetFD; FD_ZERO(&WriteSetFD); FD_SET(Fd, &WriteSetFD); if (select(Fd + 1, NULL, &WriteSetFD, NULL, NULL) < 0) { Error(strerror(errno)); } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int CommFd, TtyFd; struct termios TtyAttr; struct termios BackupTtyAttr; int DeviceSpeed = B115200; int TtySpeed = B115200; int ByteBits = CS8; const char *DeviceName = "/dev/ttyS0"; const char *TtyName = "/dev/tty"; int OutputHex = 0; int OutputToStdout = 0; int UseColor = 0; opterr = 0; for (;;) { int c = getopt(argc, argv, "d:s:t:7xoch"); if (c == -1) break; switch(c) { case 'd': DeviceName = optarg; break; case 't': TtyName = optarg; break; case 's': if (optarg[0] == 'd') { DeviceSpeed = SerialSpeed(optarg + 1); } else if (optarg[0] == 't') { TtySpeed = SerialSpeed(optarg + 1); } else TtySpeed = DeviceSpeed = SerialSpeed(optarg); break; case 'o': OutputToStdout = 1; break; case '7': ByteBits = CS7; break; case 'x': OutputHex = 1; break; case 'c': UseColor = 1; break; case '?': case 'h': default: PrintUsage(); } } if (optind != argc) PrintUsage(); CommFd = open(DeviceName, O_RDWR, 0); if (CommFd < 0) Error("Unable to open device"); if (fcntl(CommFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK) < 0) Error("Unable set to NONBLOCK mode"); memset(&TtyAttr, 0, sizeof(struct termios)); TtyAttr.c_iflag = IGNPAR; TtyAttr.c_cflag = DeviceSpeed | HUPCL | ByteBits | CREAD | CLOCAL; TtyAttr.c_cc[VMIN] = 1; if (tcsetattr(CommFd, TCSANOW, &TtyAttr) < 0) Warning("Unable to set comm port"); TtyFd = open(TtyName, O_RDWR | O_NDELAY, 0); if (TtyFd < 0) Error("Unable to open tty"); TtyAttr.c_cflag = TtySpeed | HUPCL | ByteBits | CREAD | CLOCAL; if (tcgetattr(TtyFd, &BackupTtyAttr) < 0) Error("Unable to get tty"); if (tcsetattr(TtyFd, TCSANOW, &TtyAttr) < 0) Error("Unable to set tty"); for (;;) { unsigned char Char = 0; fd_set ReadSetFD; void OutputStdChar(FILE *File) { char Buffer[10]; int Len = sprintf(Buffer, OutputHex ? "%.2X " : "%c", Char); fwrite(Buffer, 1, Len, File); } FD_ZERO(&ReadSetFD); FD_SET(CommFd, &ReadSetFD); FD_SET( TtyFd, &ReadSetFD); # define max(x,y) ( ((x) >= (y)) ? (x) : (y) ) if (select(max(CommFd, TtyFd) + 1, &ReadSetFD, NULL, NULL, NULL) < 0) { Error(strerror(errno)); } # undef max if (FD_ISSET(CommFd, &ReadSetFD)) { while (read(CommFd, &Char, 1) == 1) { WaitFdWriteable(TtyFd); if (write(TtyFd, &Char, 1) < 0) { Error(strerror(errno)); } if (OutputToStdout) { if (UseColor) fwrite("\x1b[01;34m", 1, 8, stdout); OutputStdChar(stdout); if (UseColor) fwrite("\x1b[00m", 1, 8, stdout); fflush(stdout); } } } if (FD_ISSET(TtyFd, &ReadSetFD)) { while (read(TtyFd, &Char, 1) == 1) { static int EscKeyCount = 0; WaitFdWriteable(CommFd); if (write(CommFd, &Char, 1) < 0) { Error(strerror(errno)); } if (OutputToStdout) { if (UseColor) fwrite("\x1b[01;31m", 1, 8, stderr); OutputStdChar(stderr); if (UseColor) fwrite("\x1b[00m", 1, 8, stderr); fflush(stderr); } if (Char == '\x1b') { EscKeyCount ++; if (EscKeyCount >= 3) goto ExitLabel; } else EscKeyCount = 0; } } } ExitLabel: if (tcsetattr(TtyFd, TCSANOW, &BackupTtyAttr) < 0) Error("Unable to set tty"); return 0; } |
|
2.7 UDP Network Programming
| 드라이버 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/linux-2.6.36/drivers/net/ |
| 드라이버 소스 파일 이름 | dm9000.c |
| Device Name | eth0 |
| 소스 디렉토리 | /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/examples/udptak |
| 예제 이름 | udptalk.c |
| 예제 실행 파일 이름 | udptalk |
| Test program compiled x86 version and arm version available, and its source code is exactly the same | |
예제의 전체 코드는 소스파일을 참조하세요. |
|